Results
Deliverables
D1.1 Use Cases, Ecosystem Analysis and KVIs/KPIs for OC1 and OC2 | December 2024
D1.2 IMAGINE-B5G Reference Architecture | December 2024
D1.3 Use Cases, Ecosystem Analysis and KVIs/KPIs for OC3 | September 2025
D1.4 IMAGINE-B5G Final Reference Architecture (EC review pending) | September 2025
D2.1 IMAGINE-B5G Initial Integrated Platform | August 2023
D2.2 IMAGINE-B5G Updated Integrated Platform | December 2024
D2.3 APIs for vertical interaction | December 2024
D2.4 IMAGINE-B5G Final Integrated Platform (EC review pending) | December 2025
D2.5 Final APIs for vertical interaction (EC review pending) | December 2025
D3.1 Slice-based Vertical Service Design, Interim Version | December 2024
D3.2 Vertical Trials Preparation, Interim Version | December 2024
D3.3 Trials and Pilots Demonstrations over the IMAGINE-B5G Platform, Interim version | December 2024
D3.4 Slice-based Vertical Service Design, Final Version (EC review pending) | August 2025
D3.5 Vertical Trials Preparation, Final Version (EC review pending) | August 2025
D3.6 Trials and Pilots Demonstrations over the IMAGINE-B5G Platform, Final version | January 2026
D4.1 Security Validation of the IMAGINE-B5G Platform (SEN) | December 2024
D4.2 Initial Validation of B5G Core Technologies | May 2024
D4.3 Final Security Validation of the IMAGINE-B5G Platform | March 2026
D4.4 Final Validation of B5G Core Technologies, Architectures and Ecosystems | March 2026
D4.5 Intermediate Validation of B5G Core Technologies, Architectures and Ecosystems | December 2024
D5.1 Platform On-Boarding User Manual (SEN) | November 2023
D5.2 OC2 Managment Process and Open Call 1 User Experience (SEN) | December 2024
D5.3 OC3 Management Process and OC2 and OC3 User Experiences (SEN) | January 2026
D6.1 Initial Plan for Exploitation, Standardisation and Dissemination | May 2023
D6.2 Exploitation, Standardisation and Dissemination Report, Interim Version | December 2024
D6.3 Contribution to Open-Source Solutions | November 2025
D6.4 Business Models for IMAGINE-B5G Vertical Use Cases | December 2024
D6.5 Report on Open Datasets (EC review pending) | January 2026
D6.6 Exploitation, Business Models, Standardisation and Dissemination Report, Final Version | March 2026
D7.1 Project Management and Administration Guidelines (SEN) | January 2023
D7.2 Interim Data Management Plan (SEN) | December 2024
D7.3 GDPR Handbook (SEN) | June 2023
D7.4 Mid-term Management Report (SEN) | March 2024
D7.5 Final Management Report (SEN) | March 2026
D7.6 Final Data Management Plan | March 2026
D7.7 OC2 Ethics Assessment, OC1 EEAB evaluation (SEN) | December 2024
Results
Trials
Coming soon…
Results
Standardisation
The project has worked towards actively contributing to Standards in different SDO/WG.
The table and graph below summarise the results achieved so far.
SDO/WG name/ID | Count of Contribution title/ID |
3GPP | 54 |
BFF | 10 |
ETSI | 9 |
O-RAN Alliance | 6 |
Grand Total | 79 |
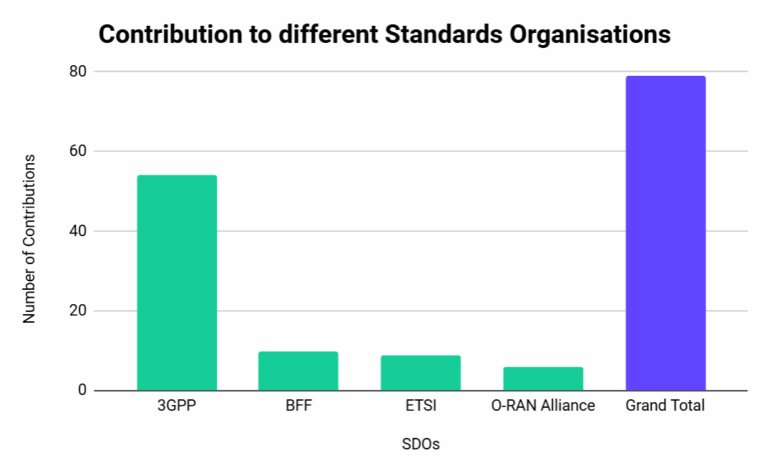
The list of standards contributions made so far can be found here for public consultation.
Results
Datasets
| ## | Dataset title | Publishing date | Dataset Description |
| 1 | 5G Performance Evolution | November 2024 | Dataset – The Chronicles of 5G Non-Standalone: An Empirical Analysis of Performance and Service Evolution |
| 2 | 5G Interactivity Dataset | December 2024 | Dataset – A Standard-compliant Assessment of Beyond-eMBB QoS/QoE in 5G Networks |
| 3 | Fire Detection Dataset | November 2025 | Rinisoft’s synthetic image dataset was created using the mask-guided diffusion framework from the paper 2FLAME Diffuser: Wildfire Image Syntheses using Mask Guided Diffusion’ |
| 4 | Remote Driving Dataset in UPV’s 5G Private network (n40) | January 2026 | KPIs collected during the remote driving of a robot in the IMAGINE-B5G Spanish facility |
Results
Publications
Consortium
Every new mobile communication generation comes with the emergence of novel applications and services. The fifth-generation (5G) is not an exception, its increased performance and flexibility are expected to provide support for a plethora of utilization scenarios, where the network can be tailored, in runtime, to the particular requirements of each use case. In particular, 5G is gaining the attention of different vertical industries as an enabler of Industry 4.0. However, adopting these technologies requires novel business models for delivering communication services. Moreover, 5G deployments are still in early stages, with novel functionalities expected to gradually emerge over the next few years. The 5GAIner laboratory provides a 5G experimentation en-vironment for the different stakeholders taking part in the 5G ecosystem. The goal is to facilitate vertical markets’ digital transition to 5G by providing an environment for easy inno-vation, development, and experimentation. In this context, the paper describes the existing infrastructure, provides some initial performance results, summarises the learned lessons, and outlines the expected evolution path.
Check out the paper here.
The rapid increase in mobile network traffic has led to the dense deployment of network cells and the introduction of technologies such as massive Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (m-MIM O) to achieve high gain and spectral efficiency. However, these benefits come with a significant growth in Operational Expenditure (OPEX) and energy consumption, which remains a major challenge in beyond 5G and 6G networks. In this paper, we employ Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) techniques to efficiently switch off cells and mute MIMO antenna elements at some specific times to achieve a higher gain in terms of Energy Saving (ES) and the number of network changes without majorly affecting user satisfaction. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that our proposed method called Smart Energy Efficiency using DRL (SEEDRL) saves power by 8.99% and significantly reduces the number of ES state changes by 22.83% compared to its counterpart the threshold-based algorithm.
Check out the paper here.
5G technologies are considered a cornerstone of the advent of the next industrial revolution. Promising performance improvements, along with advanced features and assurances in terms of reliability, flexibility and isolation, are expected to enable the realization of diverse and novel use cases, fostering industrial automation with optimized production lines and manufacturing systems. This document shares the experience and knowledge using a 5G SA network for industrial applications. Concretely, the paper examines whether and how the available technology could fulfil the demanding industry requirements, namely in terms of isolation, flexibility and performance. This gap analysis revealed 5G QoS mechanisms as a key driver towards 5G for industry. Thus, a comprehensive analysis of the existing mechanisms and their impact on the network performance are presented, serving as a reality check of 5G SA Release 15 technologies. Although results showed promising possibilities to support industrial deployments, there is still a gap between what’s achievable and what is expected from 5G that will be gradually filled by the introduction of novel features in the upcoming releases. In general, the contributions and insights presented in this paper are considered to be valuable for industry, standards development organizations, manufacturers, and the wider 5G ecosystem. Moreover, this paper serves as a foundational component within a larger endeavour of automating network slicing mechanisms for industrial applications.
Check out the paper here.
IMAGINE-B5G (Advanced 5G Open Platform for Large Scale Trials and Pilots across Europe) is an SNS Phase-1 Stream-D project which aims to implement an advanced and easily accessible end-to-end (E2E) B5G platform for large-scale trials and pilots providing a set of B5G applications, enabled by the integration of advanced 5G disrupting technologies. In this paper, we present the seven main vertical use cases targeted in IMAGINE-B5G along the four advanced 5G experimental facilities located in Norway, Spain, France, and Portugal. In addition, the onboarding of third parties (such as SMEs, industry, and researchers) for both vertical experiments and platform extensions through open calls is part of the IMAGINE-B5G road map. To that extent, we provide an overview of the 15 projects that were chosen for financing in the first open-call.
Check out the paper here.
The proliferation of virtual reality (VR) interaction in the wake of the Metaverse trend will place an increasing number of applications and services into virtual environments (VEs). Over the recent years, interactions with the VE have been studied intensely, but very frequently, such interactions are focused on stationary users or users who leverage specialized contraptions to act in the VE (e.g., omni-directional treadmills). The free movement in the VE tends to be achieved by controller input, which creates a huge hurdle to enter and act in it in a natural manner. The target of this study is the translation of the natural walking motion from the real environment (RE) into the VE. In particular, we aim to explore to which extent redirected walking (RW) is achievable without being noticed by the users. Towards this goal, we test two RW methods, i.e., rotation gain and curvature gain. According to the responses of the participants in our study, we find that there is a statistically significant difference with 90% confidence between the levels of gains for rotation gain. On the other hand, levels of gains for curvature gain are not noticeable (i.e., no statistically significant difference is observed).
Check out the paper here.
Fifth Generation (5G) networks are becoming the norm in the global telecommunications industry, and Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) are currently deploying 5G alongside their existing Fourth Generation (4G) networks. In this paper, we present results and insights from our large-scale measurement study on commercial 5G Non Standalone (NSA) deployments in a European country. We leverage the collected dataset, which covers two MNOs in Rome, Italy, to study network deployment and radio coverage aspects, and explore the performance of two use cases related to enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) and Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC). We further leverage a machine learning (ML)-based approach to model the Dual Connectivity (DC) feature enabled by 5G NSA. Our data-driven analysis shows that 5G NSA can provide higher downlink throughput and slightly lower latency compared to 4G. However, performance is influenced by several factors, including propagation conditions, system configurations, and handovers, ultimately highlighting the need for further system optimization. Moreover, by casting the DC modeling problem into a classification problem, we compare four supervised ML algorithms and show that a high model accuracy (up to 99%) can be achieved, in particular, when several radio coverage indicators from both access networks are used as input. Finally, we conduct analyses towards aiding the explainability of the ML models.
Check out the paper here.
The development of 5G and Beyond 5G (BSG) technologies relies on the availability of experimentation facil-ities that can evaluate and validate the performance of these technologies. It is of great interest and challenge to design, deploy and operate large-scale experimentation platforms to meet the high requirements of various vertical use cases for the 5G services. This paper describes an i-CORA platform that we build with multiple partners in Norway to support several EU-funded projects (5GMediaHUB, IMAGINE-B5G, FIDAL and COMMECT) and vertical use cases. The platform is cloud-native and consists of four parts: a multi-vendor end-to-end 5G network with three RAN sites serving general use cases, two mobile private networks (MPNs) and three Networks on Wheels (NOWs) serving dedicated verticals, and an open source platform composed of open source solutions. i-CORA offers both advanced standalone 5G services and value-added services (e.g., security and testing) to verticals in Public Protection and Disaster Relief (PPDR), media, eHealth, Industry 4.0, etc. In this paper, we address the challenges and lessons learned during the implementation and operation of the i-CORA platform.
Check out the paper here.
5G commercialization relies on validating the vertical use cases and selecting the ones creating values for both mobile operators and vertical stakeholders. To transfer the validations to commercialization more quickly, it is important to build a 5G platform not only with a similar scale and reliability as a commercial 5G but also capable of offering advanced beyond 5G services. In this paper, we propose an Experiment-as-a-Service (EaaS) framework which systematically offers four types of testing services, integration, functional, performance, and security testing. Then the iCORA (innovative, cloud-native, open, robust and automated) platform is presented to demonstrate how the EaaS framework could be realized in a large-scale 5G experimentation platform, which offers both diversity and flexibility for testing and experiments. A media use case is used to exemplify how the EaaS tailors the iCORA network to support various demands of vertical use cases and meet their KPIs.
Check out the paper here.
Fifth Generation (5G) systems have been commercially available worldwide for at least a couple of years, with mid-band Non-Standalone (NSA) being the deployment mode preferred by Mobile Network Operators (MNOs). Empirical analyses have provided so far key insights on 5G NSA performance from different perspectives, but most of these works consider short time periods to drive conclusions. In this paper, we investigate the evolution of 5G NSA considering deployment, performance, and services, including positioning. We perform a large-scale measurement campaign in two phases (2021 and 2023), covering six MNOs in two European countries, Italy and Sweden. Our results show significant differences in network deployment and performance, with increasing network density and frequencies but, at times, decreasing downlink throughput performance. For the latter, we identify worse radio coverage and connectivity issues as root causes. By using a standardized methodology, we also evaluate the performance of new services such as real-time gaming and augmented/virtual reality, and reveal that stable 5G connectivity is key to meet their requirements. Similarly, we highlight the negative effects of roaming on performance. Finally, we evaluate 5G fingerprinting positioning systems and show that a higher accuracy is achievable in denser 5G deployments.
Check out the paper here.
The transition to Industry 4.0 introduces new use cases with unique communication requirements, demanding wireless technologies capable of dynamically adjusting their performance to meet various demands. Leveraging network slicing, 5G technology offers the flexibility to support such use cases. However, the usage and deployment of network slices in networks are complex tasks. To increase the adoption of 5G, there is a need for mechanisms that automate the deployment and management of network slices. This paper introduces a design for a network slice manager capable of such mechanisms in 5G networks. This design adheres to related standards, facilitating interoperability with other software, while also considering the capabilities and limitations of the technology. The proposed design can provision custom slices tailored to meet the unique requirements of verticals, offering communication performance across the spectrum of the three primary 5G services (eMBB, URLLC, and mMTC/mIoT). To access the proposed design, a Proof-of-Concept (PoC) prototype was developed and evaluated. The evaluation results demonstrate the flexibility of the proposed solution for deploying slices adjusted to the vertical use cases. Additionally, the slices generated by the PoC maintain a high TRL (Technology Readiness Level) equivalent to that of the commercial-graded network used.
Check out the paper here.
Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communications are constrained by 3GPP technical specifications and country-specific spectrum regulations. V2X occurs mostly on New Radio Unlicensed (NR-U) spectrum. A specific bandwidth in the public spectrum is also available, but it is often owned entirely by one operator and is limited in bandwidth. This includes Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) services, such as those needed by autonomous vehicles. Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) like GPS or Galileo offer high-accuracy location but have drawbacks, as the information is limited to the individual vehicle and not securely shared. This exchange of position information is vital for cooperative maneuvers and to counter satellite signal loss. It is expected that, in the mid to long term, municipalities and highways will have dedicated private 5G networks for V2X operations, including positioning services. This paper provides a comprehensive review of precise positioning services for ITS in 5G private networks, examining their role in V2X scenarios. It also explores hybrid positioning systems that combine 5G and GNSS technologies. This study offers a roadmap for the evolution of ITS and V2X communications.
Check out the paper here.
Check out the paper here.5th Generation (5G) mobile systems are being deployed to address the Quality of Service and Experience (QoS/QoE) requirements of several use cases, including enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) and Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC). While eMBB performance testing inherits well-established methodologies and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), beyond-eMBB services (i.e., URLLC and eMBBURLLC real-time applications) are often tested by adopting simplistic or in-house methodologies, which do not help towards accurate assessment and comparison. In this paper, we fill this gap by providing a detailed analysis of a methodology, recently standardized by the International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T), that targets systematic performance evaluations of beyond-eMBB services. The methodology relies on the definition of a QoE KPI, i.e., the interactivity score (i-score), on top of three QoS KPIs measuring service latency, stability, and continuity. To this aim, we perform a multi-service measurement campaign on two 5G networks across two cities in Sweden, during which we run a large number of tests compliant with the ITU-T methodology, and analyze the collected data. Our results empirically validate the methodology, showcasing its ability of capturing heterogeneous service characteristics and requirements, as well as the interdependencies between i-score and QoS KPIs, and the impact of different factors on QoS/QoE performance, including user mobility, connection capability, and server location.
Check out the paper here.
5G network is expected to be highly flexible, enabling its adjustment according to user requirements. To achieve this, 5G leverages network slicing, allowing the division of the network infrastructure into different slices with completely different communication performances. However, this flexibility is not easily achieved, requiring the use of available 5G features, Quality of Service (QoS) parameters, and technologies to adapt the communication performance according to the user requirements. Furthermore, to foster wider adoption of 5G by verticals, it is crucial to simplify the network configuration process by providing common interfaces that accept attributes familiar to vertical users. In this line, having a vertical-oriented network slice manager capable of automating the deployment of slices in 5G networks is crucial. One of the key elements involved in creating such a system is a mapping between common communication attributes and available 5G configuration parameters and features. This mapping facilitates the adjustment of communication performance to meet vertical requirements. With this in mind, the document explores the realisation of such a mapping. First, it analyses the communication attributes defined by well-known organisations (e.g., 5G-ACIA, and 5GDNA); these attributes define the performance requirements of network slices or industrial use cases. Then, it maps these attributes to standardised R17 5G functionalities. The mapping is followed by a validation using the 5GAIner infrastructure (part of the IMAGINE-B5G experimental facilities), a real-world commercial-grade 5G Standalone (SA) network. The results showcase the feasibility of using this mapping to realize vertical slices.
Check out the paper here.
The paper presents an experimental testbed architecture that combines Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) and 5G cellular systems. This testbed was set up in the city of Gaia, Portugal, to address the challenge of developing a system that can provide real-time precise positioning for mobile users in urban canyons and other challenging conditions.The architecture uses positioning methods like Single Point Positioning (SPP), Precise Point Positioning (PPP), and Double Difference GNSS to overcome issues such as ionospheric delay, clock biases, and multipath commonly faced by traditional GNSS systems. A key component of the testbed is a 5G-based Location Management Function (LMF) that enhances GNSS data in real-time to minimize Time-to-First-Fix (TTFF) position estimation and improve geolocation accuracy in environments where GNSS signals may be weakened or obstructed. This system dynamically adjusts satellite and atmospheric data sent via 5G to the mobile platform (e.g., a vehicle or other UE) for more accurate geolocation.The combination of GNSS and 5G in this hybrid environment demonstrates novel potential in positioning technology. The study shows that 5G-assisted GNSS can significantly reduce error vectors, marking a breakthrough in real-time positioning solutions. The next phase involves testing the system in a moving scenario to confirm its effectiveness in vehicular and smart city applications. This research contributes to the literature by highlighting the potential of combining GNSS and 5G technologies to overcome the limitations of standalone GNSS systems, reinforcing the way for future positioning systems.
Check out the paper here.
Next-generation beyond 5G networks face significant challenges in ensuring resilient connectivity and low-latency performance for critical applications in dynamic and dense environments. This paper presents a Graph Convolutional Network (GCN)-based model to optimize handover decisions by predicting the most suitable gNodeB (gNB) for user connection in real-time. Leveraging historical connectivity data and network conditions, the model forecasts gNB connectivity and incorporates a threshold mechanism to reduce unnecessary handovers and mitigate the “ping-pong” effect. A graph representation of a real 5G dataset is constructed, where nodes represent gNBs with connectivity attributes, and edges capture potential handovers weighted by connectivity differences. The results demonstrate that the proposed GCN model improves the network resilience by ensuring stable connectivity and minimizing disruptions, achieving enhanced user experience without increasing handover frequency. This study underscores the potential of machine learning-driven resilience mechanisms in next-generation networks, offering a robust framework for dynamic connectivity management in high-mobility and latency-sensitive scenarios.
Check out the paper here.
Mixed Reality (MR) has launched from science fiction but its entrance
in reality can reshape our society. By combining the physical and virtual worlds, it provides novel ways of immersive interactions
and experiences and by these means enables a new generation of
applications. The most exciting and challenging ones support collaborative, multi-user operation in large geographical scale, require
real-time environment comprehension and high visual fidelity. The
success or failure is definitely impacted by the capabilities and
performance limits of edge cloud platforms and 5G/6G networks
providing the offloading features for CPU/GPU intensive MR functions. In addition, the desired quality of user experience calls for further mechanisms at the application level hiding the consequences
of varying network characteristics. In this paper, we propose a
novel edge cloud based architecture for future remote-rendered MR
applications supporting low-latency immersive interactions. Our
contribution is threefold. First, the system architecture is presented
focusing on the remote rendering, 3D simulation and environment
detection control loops. Second, we highlight the main features
of our proof-of-concept prototype and our dedicated application,
namely the Mixed Reality version of a Rocket League inspired game.
Third, the concepts are validated via experiments in a Beyond 5G
infrastructure where we analyze the operation and latency characteristics of the overall system. In addition, the quality of the user experience is also evaluated via real-life experiments conducted as part of a student competition. The results show that the latency and jitter characteristics of the most sensitive render loop can be managed efficiently together by a network-level control (slice priorities) and an application-level (dynamic jitter buffer) mechanism.
Check out the paper here.
5G network is expected to provide mMTC (massive Machine Type Communications or massive Internet of Things [mIoT]) slices in the near future, coinciding with expectations for a significant increase in the IoT global market. Many new IoT use cases are anticipated to be deployed using 5G which requires mMTC performance. Release 17 introduces several mMTC features. However, as of release 19, 3GPP does not claim full support of mMTC slices.
Even if 5G cannot fully support mMTC network slices yet, several network features are already standardized and included in commercial-graded 5G networks. These features allow for the reconfiguration of the network to provide communication performance close to what is provided in mMTC slices. This paper analyzes and evaluates several of these features, demonstrating that current 5G networks are already capable of supporting some of the mMTC use cases expected to be deployed in the future.
Check out the paper here.
This paper investigates the development of a solution for Edge Internet Traffic Steering (EITS), focusing on optimizing the performance of services at the network edge using Computing-Aware Traffic Steering (CATS) principles. Motivated by the increasing demand for low-latency connectivity, high bandwidth, resource availability, link redundancy, and efficient memory and CPU usage optimization, this research addresses the limitations of existing traffic steering approaches in meeting the static or dynamic requirements of edge services. The proposed solution leverages network and compute metrics to direct traffic to the most suitable service instance, enhancing overall performance through the use of OpenAirInterface 5G Core Network. The practical implementation of a video streaming use case demonstrated the efficacy of the solution.
Check out the paper here.
Haptic teleoperation systems mark a critical breakthrough in remote manipulation technologies, delivering immersive user experiences through precise control and tactile feedback. This paper aims to explore the interplay between Quality of Service (QoS) network metrics, such as latency, jitter, and packet loss, and Quality of Experience (QoE) features, including immersion, control, and engagement. This investigation is conducted through a combination of objective measurements and subjective evaluations over a private Fifth Generation Standalone (5G SA) network. In addition, it aims to realize the extent to which transport-layer protocols operating over IP, such as TCP and UDP, as well as environmental factors like indoor and outdoor settings, influence system performance.Results confirm the well-established trade-off between reliability and latency in transport protocols, with TCP offering higher reliability in controlled indoor environments, and UDP exhibiting better responsiveness in dynamic outdoor scenarios. While these findings align with existing knowledge, their empirical validation in the context of immersive haptic applications over a private 5G SA network reinforces their relevance. In addition, QoE metrics were found to be linked to QoS indicators, highlighting the importance of balancing speed, stability, and reliability. These findings provide valuable insights towards designing adaptive teleoperation systems capable of dynamically optimizing performance under diverse conditions.
Check out the paper here.
In this paper, we investigate the effects of asynchrony between the visual and haptic feedback in virtual reality (VR) on user experience, specifically focusing on understanding users’ awareness of this asynchrony and its effect on their level of satisfaction. Using Unreal Engine, we created an experimental setup to adjust the timing between these sensory inputs. Our experiment featured a VR dodge game that provides haptic feedback on the body when the player is hit by a multitude of virtual objects. Conducting a targeted, small-scale user study, we aim to understand in what ways an introduced asynchrony influences the VR experience. The results highlight the perceptibility of asynchrony, which significantly affects the overall user experience. Nonetheless, we also find an asymmetry that benefits scenarios where haptic feedback precedes visual cues. Furthermore, our findings suggest that users can generally accept minor levels of asynchrony without significant disadvantages to their satisfaction. However, it is interesting to note that even when users cannot explicitly identify any asynchrony, they might still experience a slight decrease in satisfaction.
Check out the paper here.
The evolution of 5G and B5G networks is revolutionizing mobile communications and enabling new use cases. Consequently, vertical industries are relying more on advanced applications that can leverage the potential of such innovations – the so-called Network Applications. However, testing frameworks for these advanced Network Applications remain scarce, limiting the adoption of such applications. This work proposes a framework to orchestrate, test, and validate these applications, introducing specific test cases to validate their functionality.
Check out the paper here.
The evolution of 5G and B5G technologies introduced high levels of programmability, control, and flexibility to wireless networks. However, the integration of these capabilities with industry-specific applications still remains challenge. The CAMARA initiative addresses this by standardizing APIs to simplify the interaction between applications and 5G/B5G network functionalities. Our demonstration introduces the concept of CAMARA APIs as a Service, an approach that enables telecommunication operators and service providers to offer these APIs with minimal development effort. We showcase how telecom operators can address Quality on Demand use cases through the ordering of a CAMARA API to manage the QoS of User Equipment within a 5G standalone commercial graded network. This demonstration highlights the potential of CAMARA as a Service to accelerate the adoption of CAMARA APIs and enhance the pro-grammability of 5G/B5G services for the various industries.
Check out the paper here.
The worldwide energy consumption increases every year and it shows no signs of slowing down, particularly with the high rate of adoption of electric cars. Home systems must be deployed which optimize the energy consumption of a house. This paper presents a system which is able to, given a set of tasks to perform, optimize which tasks should be performed at each time. Results showed a potential 84% decrease in the daily electrical bill when compared with a household not equipped with our task optimization mechanism, leading to a potential cost saving of 427 annually.
Check out the paper here.
Network federation is a promising approach for organizations to improve their infrastructure by pooling their resources and creating a larger, more scalable network. Despite the many benefits of network federation, there are also significant challenges that must be addressed, such as security, interoperability, and policy management. Various efforts have been underway for many years to develop common standards and protocols, to overcome these challenges. This paper provides a comprehensive overview of the challenges and opportunities of network federation, and presents the standardization efforts in the field.
Check out the paper here.
Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) is a promising paradigm that brings computational capabilities closer to end-users, enabling low-latency and high-bandwidth applications. The federation of multiple MEC platforms has the potential to create a collaborative ecosystem, facilitating resource sharing and scalability. This paper addresses the benefits of exploring the synergies between Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and MEC federation deployments, aiming to enhance the network infrastructure’s overall performance, flexibility, and responsiveness. More concretely, this work explores the integration of MEC and SDN to address performance and resource utilization challenges in congested federated MEC environments, enabling seamless service migration between MEC nodes when resource constraints arise with results showing its ability to maintain service quality under congestion.
Check out the paper here.
Modern heterogeneous networks and distributed applications deployed across the computing continuum pose significant monitoring and management challenges due to their complexity and dynamic nature. Cloud-native observability has emerged as a powerful paradigm to overcome these challenges, enabling the extraction of knowledge and operational insights by combining information from metrics, logs, and traces. At the same time, advanced Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques drive network automation toward Zero-Touch Network and Service Management (ZSM). In this work, we present FUSION, an integrated observability and analytics framework that unifies heterogeneous telemetry data and leverages AI-powered intelligence to extract knowledge, identify behavioral patterns, and increase automation. A conceptual architecture is detailed, standardizing heterogeneous data collection and fusion in a unified observability layer, while supporting the integration of advanced AI-based analytics pipelines. A prototype implementation demonstrates the use of representative AI-based methods for anomaly detection, root cause analysis, and intelligent orchestration.
Check out the paper here.
Open Call Winners
This article explores the viability of ULTRA-FAB5G, a paradigm-shifting 5G use case that aims to replace traditional wired infrastructure and dedicated devices with a wireless, private 5G edge in an industrial environment. Using the IMAGINE-B5G Portuguese experimental facility, an early proof-of-concept demonstrates the capabilities of the technology, highlighting positive results in latency, jitter, and bandwidth, as well as evaluating the inter-slice latency gap at the application level. The study will progress to integrating the proof-of-concept with real industrial equipment, paving the way for a forthcoming industrial deployment. With promising results, this research showcases the potential for improved industrial landscapes using 5G and beyond technologies and provides valuable information on the evolution roadmap of 5G technologies.
Check out the paper here.
Cognitive health issues, such as mild cognitive impairment (MCI), Parkinson’s disease, and stroke, impact millions of people worldwide. Traditional clinical assessments often require in-person visits, which can be a barrier for those in remote or underserved areas. CogNetCare is a solution designed to bridge this gap by providing a 5G-enabled digital healthcare system that integrates remote cognitive screening and physical monitoring. This solution enables early detection and continuous tracking of neurological conditions outside traditional healthcare settings. In this paper, we introduce the system’s architecture, key performance indicators (KPIs), and validation strategies, highlighting the potential impact of such an e-health solution on real-world healthcare.
Check out the paper here.
Beyond 5G and emerging 6G networks have the potential to revolutionize medical services by enabling ultra-reliable, low-latency communication, AI-driven edge intelligence, and dynamic network adaptation for real-time healthcare applications. The Drone Care Angel is an AI-driven context-aware mobile health monitoring system that utilizes Unmanned Aerial Vehicles to provide real-time surveillance and emergency detection. Equipped with high-resolution cameras, the UAV continuously monitors individuals, analyzing physiological and movement patterns to detect potential health anomalies. By integrating edge computing and AI-based analytics, DCA enables rapid anomaly detection, allowing for timely medical intervention and improved remote decision-making. To achieve its objectives, DCA leverages B5G capabilities, including Multi-access Edge Computing for low-latency AI inference and dynamic network slicing for adaptive low-latency communication to ensure seamless data transmission.
Check out the paper here.